Watch out! You Can’t Deprive Yourself of Vitamin B12

Vitamin B12 is essential for the proper formation of hematopoietic cells, the marrow cells from which all blood cells originate. It is involved in the synthesis of myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds neurons, and choline, the precursor of acetylcholine, this neurotransmitter essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It also interacts with the metabolism of vitamin B9.
This vitamin is exclusively synthesized by microorganisms, such as the bacteria present in the intestines of animals. Our intestinal microbiota produces it but our intestines are not able to absorb it: intake through food or food supplements is essential.
Where to find it?
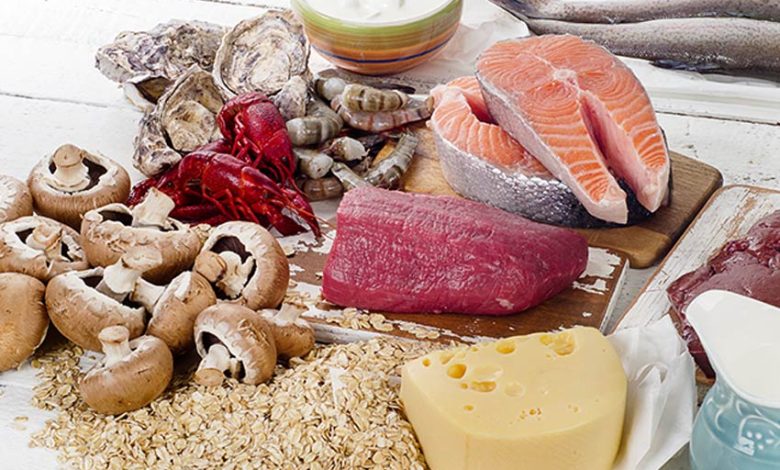
Vitamin B12 is found in offal (liver, kidney) and in meat, but also in milk and products resulting from its fermentation (yogurts, cheeses), eggs, large fish (tuna, salmon, etc.). and seashells.
It is also present, in smaller quantities, in certain algae (nori, chlorella), mushrooms and lactofermented plant products. Brewer’s yeast, unless fortified with vitamin B12, does not contain any.
As for spirulina (which is a cyanobacterium), it produces a form that would not be well absorbed by our bodies. It is therefore not considered a reliable source of vitamin B12, as recalled by an opinion from ANSES.
When to take this vitamin?
1) In case of vegan diet or a diet very low in animal products, in order to prevent the risk of deficiency.
2) In case of proven deficiency : as for vitamin B9, vitamin B12 deficiency is expressed by anemia, with fatigue and digestive disorders, and by neurological damage with motor disorders and sensitivity, irritability, memory and speech disorders. ‘mood.
3) In case of consumption of alcohol, tobacco and/or medicationsuch as metformin (treatment of type 2 diabetes), proton pump inhibitors (PPI) or certain oral contraceptives, these substances interfering with the metabolism of vitamin B12.
4) In prevention of other diseases : vitamin B12 could prevent cardiovascular diseases and Alzheimer’s disease, its deficiency resulting in an accumulation of homocysteine, toxic for the heart and the brain. But this is not confirmed by any clinical study.
5) In case of pregnancy : in some women at risk of deficiencies, vitamin B12 may also be indicated, on medical advice.
No dose limits
The recommended intakes of vitamin B12 are 4 µg/d in adult men and women, they are higher in pregnant and breastfeeding women (4.5 and 5 µg/d), lower in children and adolescents (1 .5 – 2.5 µg/d).
Since the intestinal absorption capacities are very low, the food intake of high doses (more than 5 µg in one intake) is of no use.