Itchy skin: an early warning sign of kidney disease
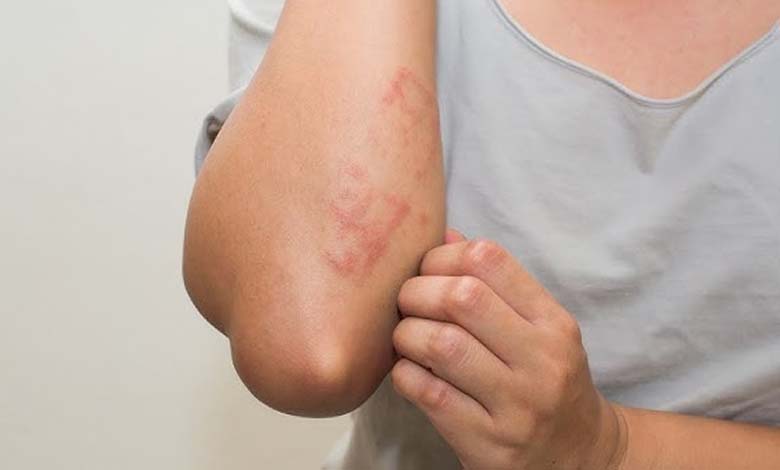
The skin, often seen merely as a protective layer, can in fact serve as a window into the body’s internal health. Among the subtle yet significant signs that deserve attention is persistent itching — a symptom that may be far more than a minor irritation. Medical research has increasingly shown that chronic itching without a clear cause can be an early indicator of kidney dysfunction.
-
Scabies outbreak raises concern in the United Kingdom
-
Is Silicone Tape Truly Effective for Scar Treatment?
The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste products and maintaining the body’s chemical balance. When their function declines, toxins and metabolic byproducts build up in the bloodstream, affecting multiple systems — including the skin. This condition, known as uremic pruritus, affects a large proportion of people with chronic kidney disease, sometimes even before an official diagnosis is made.
Renal itching tends to be widespread or localized on the arms, back, or scalp. Unlike allergic rashes or eczema, it usually appears without any visible lesions. This absence of marks often misleads patients, who may attribute it to dry skin or stress. In reality, it reflects a deeper imbalance within the body.
The mechanisms behind this phenomenon are complex. The accumulation of toxins such as urea, immune system overactivity, and the disruption of nerve endings in the skin all contribute to the sensation. In addition, imbalances in blood calcium and phosphorus — common in kidney failure — can trigger irritation through the formation of microscopic deposits beneath the skin.
Early recognition of this symptom is crucial, as it can help detect kidney disease before it reaches an advanced stage. Doctors recommend consulting a healthcare professional if itching persists for more than two weeks without a clear cause, especially when accompanied by fatigue, swelling, fluid retention, or reduced urine output.
-
How to Protect and Boost Collagen in Your Skin?
-
Reducing Sugar for Better Skin: Boosting Elasticity and Soothing Acne
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying kidney condition. Maintaining proper hydration, following a balanced diet low in phosphorus and sodium, and monitoring kidney function regularly can help slow disease progression. In parallel, topical soothing creams, antihistamines, and light-based therapies (phototherapy) may help relieve the discomfort.
Prevention remains the best approach: controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes, avoiding excessive use of painkillers, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle all contribute to protecting kidney health.
-
With Winter Approaching… 5 Tips for Treating Dry Skin
-
The Best Vitamins for Healthy and Glowing Skin
Ultimately, itchy skin is not always a harmless nuisance. It can be an early alarm — the body’s subtle way of signaling that the kidneys are under strain. Paying attention to this warning and seeking medical advice promptly can make the difference between early intervention and irreversible kidney damage.