The strange oscillations of Betelgeuse
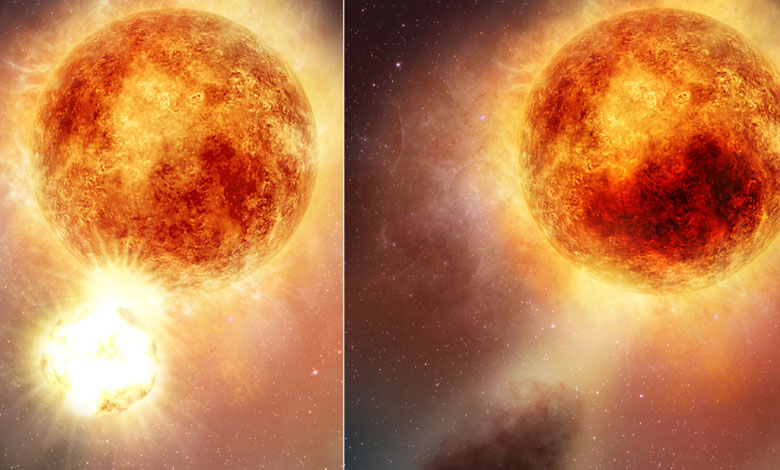
What had happened in the fall of 2019 was Betelgeuse expelling an enormous amount of matter — enough to obscure part of the star from our eyes, and give the impression of this fading. But the causes of this expulsion are deeper and probably explain why the star has not yet recovered.
The 2019 event is believed to have occurred when the star was at the peak of its 400-day cycle, coinciding with the appearance of a hotter region on its surface. The resulting expulsion of material was billions of times that of the most massive flares from our Sun. This explains why it is still apparently “unbalanced” today: it has lost its 400-day cycle of “beats” that we have known about it for two centuries. For the moment, this rhythm seems to have accelerated. And its surface oscillates in an abnormal way, astrophysicists from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and institutions in two other countries note in their study.
But beyond the astronomical curiosity that all this represents, Betelgeuse is not in good health: it is a massive star – a red supergiant – which is approaching its inevitable end of life. Some theorists predict that it will die in a final explosion—a supernova—likely to occur in “only” 10,000 years. Others place a more distant date, or speculate on a less spectacular death. In any case, the fact that it is in our vicinity – just 430 light years away, in the constellation of Orion – offers a rare opportunity to observe these strange phenomena. Another mass expulsion of matter is thus planned for 2026.
The worst case scenario – a supernova – does not represent a risk for us: it would require being 10 times closer. But the spectacle is likely to be impossible to miss in the sky.












