Continued Nicotine Addiction Among Youth
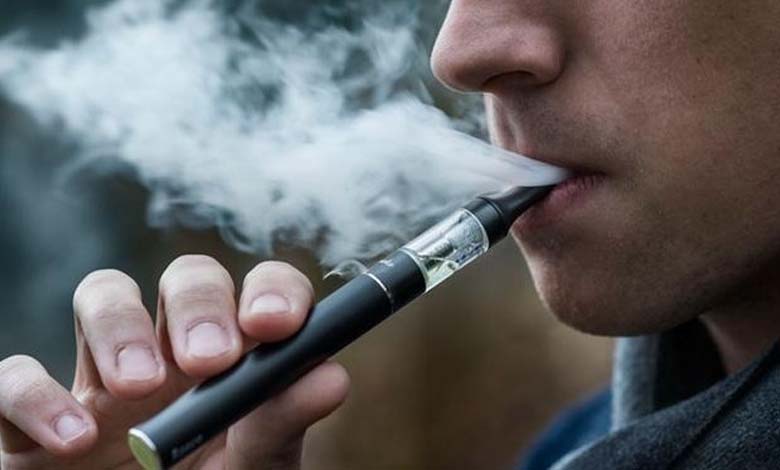

Despite concerted efforts to curb e-cigarette smoking among teenagers, recent data confirms the continued grip of nicotine addiction among youth who initiated e-cigarette use during their teenage years.
According to a report by the National Public Radio network, the appeal of single-use e-cigarettes and the wide-reaching marketing tactics employed by e-cigarette companies have contributed to the ongoing spread of e-smoking habits among this demographic, even as they transition into adulthood.
A recent study conducted in Colorado shed light on a concerning trend, where a significant portion of previously exposed teenagers continue to use e-cigarettes as adults, perpetuating what experts have termed the “e-cigarette generation” phenomenon.
One former student from the University of Colorado vividly recounts the peak of his e-cigarette addiction during his college years, stating that he began using single-use e-cigarettes at a rate of 1200 puffs per week, then it became increasingly complicated. Despite acknowledging the harmful health effects and social stigma associated with vaping, he confirmed struggling to break free from this habit due to the ingrained nature of his addiction.
Experts explain that the entrenched nature of this habit is because, for many youths, vaping has become an unconscious response after years of continuous use.
While efforts to reduce e-cigarette smoking among teenagers have seen some success, recent data shows a worrying increase in e-cigarette smoking rates among young people aged 18 to 24 between 2020 and 2022.
Dr. Delaney Royston, a primary care physician and documentary filmmaker, underscores the addictive nature of nicotine, especially concerning brain development, by facilitating the transition from teenage experimentation to persistent addiction by making e-cigarettes accessible and socially acceptable, thereby perpetuating the addiction cycle among young adults.
The exacerbation of vaping habits during the COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the multifaceted nature of the addiction crisis. Experts have pointed out the impact of social isolation and increasing anxiety on drug consumption behaviors among young people, which may escalate the prevalence of vaping habits.
Despite ongoing debates about the role of e-cigarettes in smoking cessation, data indicates that the majority of e-cigarette users among young adults did not start using them as a means to quit smoking. Stanton Glantz, a tobacco researcher, challenges claims that vaping aids smoking cessation and highlights the disproportionate distribution of vaping among youth compared to older age groups.
Despite the immense challenges posed by nicotine addiction, support from smoking cessation programs and universal design can help youth overcome the intense psychological craving associated with e-cigarette addiction, thus providing a beacon of hope amidst the widespread public health crisis.