What Happens to Your Body When You Drink Coconut Water Daily?
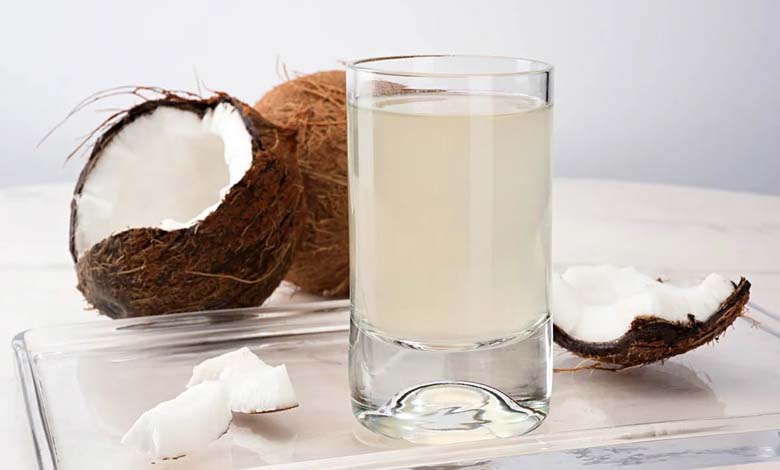

Coconut water is often promoted as a natural beverage with multiple health benefits. Extracted from young green coconuts, it is valued for its hydrating properties, electrolyte content, and healthy image. Popularized by modern nutrition trends and widely marketed worldwide, coconut water has become increasingly popular among health-conscious consumers.
Beyond marketing claims, however, what actually happens in the body when coconut water is consumed daily? Are its effects universally beneficial, or do they depend on individual metabolic profiles and dietary habits? A scientific perspective helps clarify its physiological impact.
Nutritional Composition
Coconut water consists primarily of water and contains essential electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, magnesium, and calcium. It also provides small amounts of natural carbohydrates, mainly simple sugars, along with amino acids and antioxidant compounds.
Its potassium content is particularly significant. This mineral plays a key role in fluid balance, muscle contraction, and blood pressure regulation. Compared to many sugary beverages, coconut water contains fewer calories, contributing to its reputation as a healthier alternative.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Daily consumption of coconut water can enhance hydration, especially for physically active individuals or those living in hot climates. Its electrolytes help maintain fluid balance and support proper muscle and nerve function.
After exercise, electrolyte losses through sweat can lead to fatigue, cramps, and reduced performance. Coconut water may serve as a natural rehydration option. However, for prolonged or intense physical activity, its sodium content may be insufficient compared to specialized sports rehydration solutions.
Effects on Blood Pressure
Regular intake of coconut water may contribute modestly to blood pressure regulation due to its high potassium content. Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium and supports vascular relaxation.
For individuals with mild hypertension, a potassium-rich diet can support cardiovascular stability. Nevertheless, coconut water is not a substitute for medical treatment in cases of diagnosed hypertension.
Digestive Impact
Coconut water is generally gentle on the digestive system. It contains bioactive compounds and small amounts of soluble fiber that may support digestion and promote regular bowel movements.
However, excessive intake may cause mild digestive discomfort in some individuals, partly due to its natural sugar and potassium content. Moderation remains essential.
Metabolic Effects and Blood Sugar
Although coconut water is less sugary than many commercial beverages, it still contains carbohydrates. Moderate daily consumption can fit within a balanced diet. Individuals with diabetes or blood sugar sensitivity should monitor their total carbohydrate intake.
Some research suggests that antioxidants in coconut water may help reduce oxidative stress, a factor involved in metabolic disorders. These potential benefits require further large-scale studies.
Kidney Function and Mineral Balance
The high potassium content in coconut water can support muscle and cardiovascular health. However, excessive intake may pose risks for individuals with impaired kidney function. When kidney function is compromised, potassium elimination may be reduced, increasing the risk of hyperkalemia.
Therefore, while generally beneficial for healthy individuals, coconut water should be consumed cautiously in specific medical contexts.
Weight Management and Caloric Intake
Coconut water contains fewer calories than soda and sweetened juices. Replacing high-sugar drinks with coconut water may help reduce overall caloric intake. However, it should not be viewed as a weight-loss miracle or fat-burning solution.
Its impact on body weight ultimately depends on overall dietary patterns and physical activity levels.
Conclusion
Drinking coconut water daily can support hydration, maintain electrolyte balance, and modestly contribute to blood pressure regulation. Its effects are generally positive when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced lifestyle.
However, it is neither a universal remedy nor a miracle solution. Like any dietary component, its benefits depend on individual health status, nutritional needs, and overall lifestyle. A thoughtful, personalized approach remains the key to incorporating coconut water into a healthy and sustainable diet.