Hoarseness: A Symptom That Could Indicate a Serious Illness
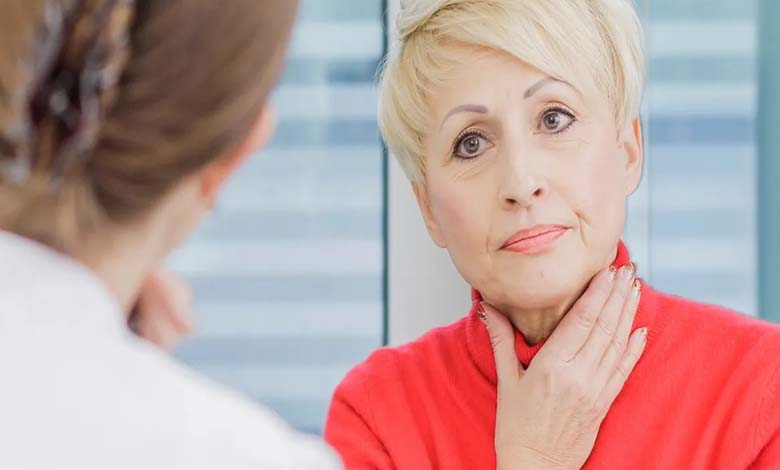

Hoarseness is often perceived as a temporary discomfort, but it can, in reality, be one of the early symptoms of a more serious condition, particularly thyroid cancer. This type of cancer, though relatively rare, is a malignant tumor that develops in the tissues of the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, which plays a key role in regulating many bodily functions by producing hormones.
-
This Habit Helps Keep Alzheimer’s Symptoms Under Control
-
“Warning” Symptoms of Dementia That May Appear in the Hands: Learn About Them
According to an article from the Russian Pravda website, while thyroid cancer is considered rare compared to other forms of cancer, early diagnosis is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of treatment. Indeed, early diagnosis can not only improve the chances of successful treatment but also reduce the risk of severe complications. This is why it is important to remain vigilant for the signs and symptoms that could indicate the presence of this disease.
Here is a detailed list of 8 signs that may suggest the disease is developing:
-
“Menopause”: Symptoms That May Appear in Your Thirties
-
Learn About “Cortisol” and the Symptoms of Its Elevation in Women
The appearance of a lump or swelling in the neck:
One of the first noticeable signs of thyroid cancer is the appearance of a lump or swelling in the front of the neck that can be felt during a physical examination. This lump may initially be soft and painless, but over time, it becomes firmer and larger. The lump’s appearance can be gradual, making it hard to detect in its early stages, and it may grow slowly without causing significant pain.
Enlarged lymph nodes:
Thyroid cancer can spread to the lymph nodes, which are small, bean-shaped structures that are crucial for the immune system’s function. Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, which can often be painless, may indicate that the cancer has begun to spread. These swollen nodes can be visible or palpable, and their enlargement can be a critical sign that further investigation is needed.
-
Early Symptoms Indicating Mental Health Issues in the Elderly
-
Sleep paralysis: Symptoms to recognize
Hoarseness or change in voice:
The tumor can press on the vocal cords, making it harder for them to vibrate properly. This can lead to noticeable changes in the voice, with one of the most common symptoms being persistent hoarseness. A hoarse or weak voice may not go away even after several days, and if this symptom persists, it is a sign that the tumor is affecting the vocal cords, and medical attention should be sought promptly.
Neck pain:
Pain in the front of the neck that may radiate to the ears is another potential symptom. This pain can vary in intensity depending on the size of the tumor and its proximity to nerves or other sensitive structures in the neck. It can also be intermittent or constant, and if it becomes severe, it may be an indication that the tumor is pressing on nerve pathways, leading to discomfort or pain.
Difficulty swallowing:
As the tumor grows, it can interfere with the normal swallowing process, causing pain or difficulty when swallowing food or liquids. This can lead to a sensation of blockage in the throat. This difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia, may also be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or pressure in the throat, which can make eating and drinking uncomfortable.
Difficulty breathing:
In some cases, if the tumor exerts significant pressure on the airways, it can cause difficulty breathing, resulting in shortness of breath or a feeling of being unable to get enough air. This can also manifest as wheezing or labored breathing, especially during physical exertion or even at rest. This symptom is particularly concerning as it may indicate that the tumor is interfering with the vital structures responsible for respiration.
-
Phagophobia – What are its symptoms and how can it be treated?
-
How to treat a sore throat? 5 reflexes to relieve symptoms
Persistent cough:
A chronic, unexplained cough that does not seem to be linked to an infection could be a sign of an underlying condition, such as thyroid cancer. The persistent cough may occur when the tumor presses against the trachea or the bronchi, causing irritation. The cough may also become dry or, in some cases, be accompanied by blood, especially in more advanced stages.
Hormonal disturbances:
The tumor can affect the thyroid gland’s ability to produce hormones, leading to symptoms of either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. These may include fatigue, weight gain, nervousness, excessive sweating, weight loss, or, conversely, unexplained weight gain. The hormonal fluctuations caused by the tumor can make these symptoms confusing and difficult to diagnose without proper medical monitoring.
-
Osteomalacia : causes, symptoms and treatments
-
Posthitis: causes, symptoms, treatments of this inflammation of the foreskin
It is important to note that the presence of one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that you have thyroid cancer. These symptoms can also be associated with other, less serious conditions. However, if any of these symptoms appear or persist, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor for a comprehensive examination. Early detection and timely treatment are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of treatment and improving the chances of recovery.