The Revolutionary Benefits of Using Robots in Surgical Operating Rooms
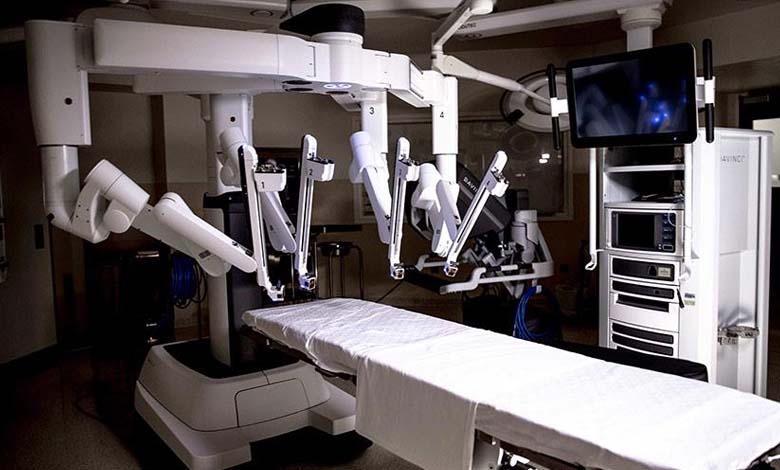
Robotic technologies continue to expand to various medical specialties, promising shorter interventions, reduced risks of complications, and improved patient recovery.
The French newspaper “Le Monde” reported that neurosurgeon Michel LeFranck from the University Hospital of Amiens recently performed a unique operation targeting isolated lower back pains without using traditional screws. Instead, he utilized a robot named Rosa to precisely burn nerve endings and discs, allowing for bone fusion.
This level of precision is achieved through meticulous planning using a digital twin of the patient, allowing seamless integration between images and the patient during surgery.
Michel LeFranck’s expertise reflects a growing trend in robotic surgery, with over 95% of his procedures performed with the assistance of Rosa, highlighting the transformative impact of robots in the medical field.
Le Monde emphasized collaborative efforts between institutions, such as Greco, a research group founded at the University Hospital of Amiens, and technological advancements from companies like Smart Robotics, which demonstrate the pioneering spirit driving these innovations.
The introduction of robots like Da Vinci, with its articulated arms resembling a giant octopus, has pushed advancements in soft tissue surgery. Originally developed for heart procedures, Da Vinci has found its place in urology due to its ability to access challenging anatomical areas.
However, the adoption of robotic technology also faces challenges, particularly in specialties like gynecology and thoracic surgery, where there are no procedural protocols and comprehensive studies to evaluate robotic interventions. Despite the hurdles, robots have had a significant impact on surgical outcomes.
Studies show a decrease in blood loss, minor complications, shorter hospital stays, reduced infection risks, and faster recovery times for patients undergoing robotic surgery compared to traditional methods. For example, robotic bladder removal led to a 50% reduction in the risk of readmission and a 77% decrease in blood clots.
Surgeons also benefit from reduced physical strain and improved dexterity, contributing to overall procedural success. Looking ahead, emerging technologies like Star, capable of performing complex procedures autonomously, promise a bright future for robotic surgery.
Le Monde highlighted collaboration between academic and industrial sectors, such as the Feros project at the University of Sorbonne, aiming to enhance robotic systems for spinal surgery. Additionally, robotic assistants, like Moon Surgical’s prototype, offer a cost-effective alternative to Da Vinci, enhancing surgical capabilities while ensuring patient safety.
In conclusion, with the ongoing evolution of robots, they promise to redefine surgical standards, making procedures safer and more precise, accessible to patients worldwide. Despite persistent challenges, continued commitment to innovation ensures that robots will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of medicine.